
Signs of Nicotine Overdose: How Much Vaping Is Too Much?
March 22, 2022
Meet Faith in Recovery’s Certified Pet Therapy Dog Luke!
April 11, 2022
Signs of Nicotine Overdose: How Much Vaping Is Too Much?
March 22, 2022
Meet Faith in Recovery’s Certified Pet Therapy Dog Luke!
April 11, 2022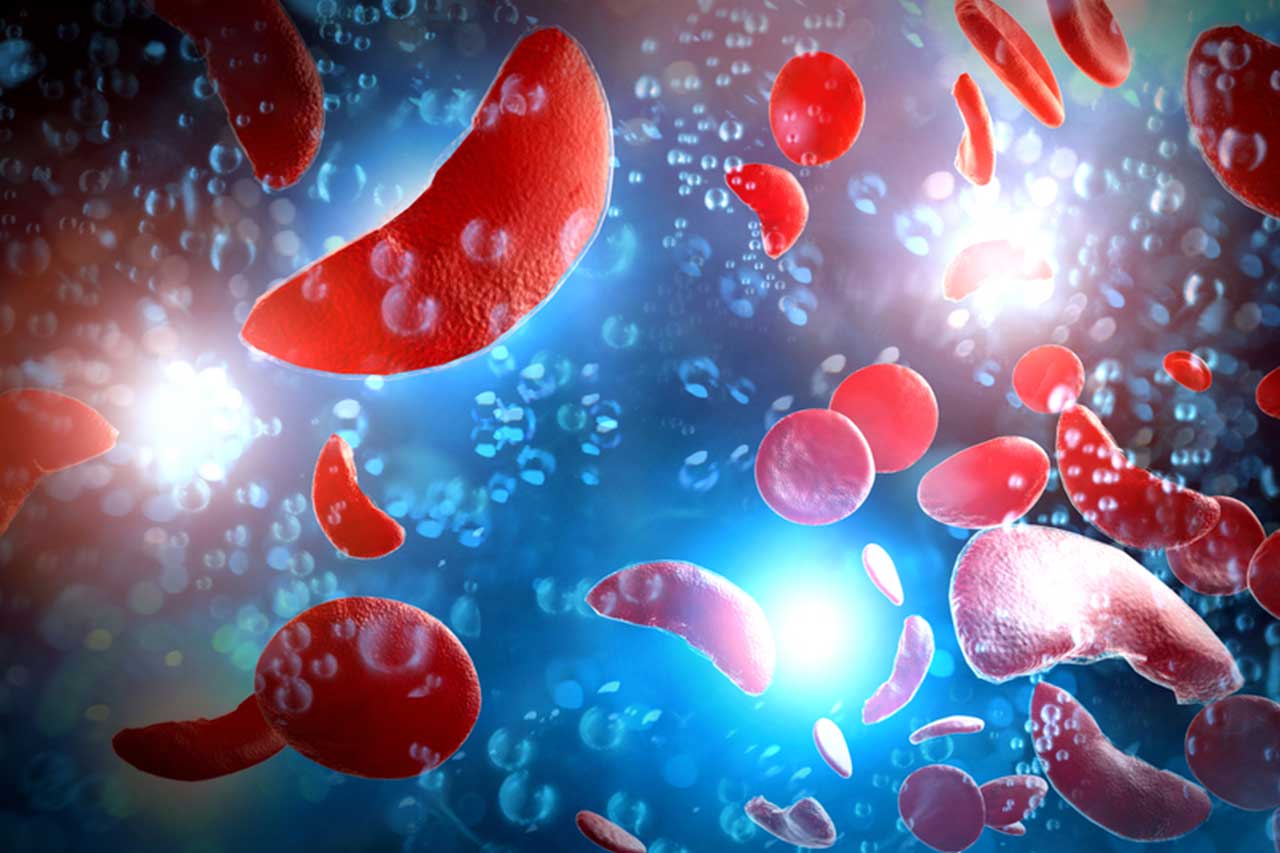
It’s widely known that alcohol leads to various health problems, ranging from allergies to alcohol intolerance to diabetes. But what is the relationship between anemia and alcohol? Can alcohol cause anemia? Can people with anemia drink?
What Is Anemia?
Anemia is a condition in which the blood doesn’t contain enough healthy red blood cells and is caused by a lack of red blood cells in the body or dysfunctional red blood cells. This leads to symptoms like fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, dizziness, and rapid heart rate.
There are three different types of anemia:
- Sickle cell anemia: Causes red blood cells to be shaped like crescents. As a result, they may break down more quickly or more easily clog small blood vessels. This can reduce oxygen levels and cause pain.
- Vitamin deficiency anemia: Deficiency in vitamin B-12 and folate both play a role in low red blood cell count. Some types of vitamin deficiency anemia include megaloblastic anemia and pernicious anemia.
- Iron deficiency anemia: This is a type of anemia that results from low iron levels in the blood. Iron deficiency anemia may develop as a result of a low-iron diet, heavy menstruation, frequent blood donation, and endurance training.
The most common type of anemia is iron deficiency anemia, which occurs when a person’s iron levels are low, and blood loss is often the cause. When the body loses blood, it draws water from tissues outside of the bloodstream to keep the blood vessels full. However, this additional water dilutes the blood, reducing red blood cell count and causing anemia.
Blood loss can be acute, rapid, or chronic. Chronic blood loss is most often responsible for anemia, which can result from a stomach ulcer, cancer, or another type of tumor. Other possible causes of anemia related to blood loss include:
- Ulcers
- Leukemia (cancer)
- Thalassemia
- Hemorrhoids
- Gastritis
- Aspirin and ibuprofen
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
Can Alcohol Cause Anemia?
So, what do anemia and alcohol have to do with each other? Red blood cells are needed to carry and deliver oxygen throughout the body. A person with anemia has a low red blood cell count, which can lead to various other problems in extreme circumstances.
Alcohol can cause anemia, specifically a type of anemia called alcohol macrocytic anemia. Otherwise known as megaloblastic anemia, alcoholic macrocytic anemia results from a folate deficiency caused by malnutrition and an antifolate action of alcohol. Antifolate refers to the folate-blocking actions of alcohol.
Low folate levels are the most common cause of low red blood cell count in hospitalized alcoholics. Heavy alcohol drinking is more commonly responsible for macrocytosis.
Alcohol-induced anemia can either be a short or long-term problem, depending on how heavily a person drinks. While anemia can occur after heavy drinking, anemia associated with alcoholism or chronic alcohol use is more common, along with other long-term issues like an alcoholic-liver disease. Alcoholic anemia can occur for various reasons. Below are some of the ways alcohol affects red blood cell production.
Bone Marrow Suppression
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found in the center of the bones, which plays a key role in red blood cell creation. Bone marrow produces stem cells, which develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Diseases like leukemia affect bone marrow, as well as red blood cell production. In particular, leukemia is a type of cancer that triggers the production of excessive and abnormal white blood cells, which disrupts the production of red blood cells. This, in turn, can lead to anemia. Alcohol can impact red blood cell production and cause anemia by decreasing the number of precursor cells in bone marrow. As a result, fewer mature red blood cells will be made.
Enlarged Red Blood Cells
Alcohol can also impact red blood cell maturation, which can lead to undeveloped and abnormally shaped or dysfunctional red blood cells. When alcohol enlarges red blood cells, they are more susceptible and more likely to be destroyed quicker than normal cells.
Malnutrition
Alcohol can also impact how the body absorbs nutrients. Alcohol-induced malnutrition usually leads to folic acid deficiencies, which impact the body’s ability to form red blood cells. This is why vitamin folate is usually used to treat anemia.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Alcohol can also increase the risk of internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Drinking too much alcohol can wear down the digestive tract, tearing away at tissue and causing it to become sensitive enough to tear. These tears are called Mallory-Weiss tears and can result in heavy internal bleeding, which in turn can lead to anemia.
Alcoholic Anemia Symptoms
Alcoholic anemia symptoms may vary depending on the cause and severity of anemia. Because the human body and all of it’s parts require oxygen to function properly, anemia can have serious side effects if it’s not treated properly or swiftly. With that said, if you’re a heavy drinker, then watch out for these alcohol anemia symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness and dizziness
- Pale or yellow skin
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pains
- Abnormal or rapid heartbeat
- Cold hands, feet, or other extremities
- Headaches
- Reduced mental and physical capacity
Fortunately, anemia from alcohol use is reversible. Most people will see an improvement in their red blood cell count a few weeks after they stop drinking alcohol. If alcohol-induced anemia was the result of low folic acid, the individual might be prescribed a supplement to offset this imbalance. However, the main issue is that alcohol can impair the body’s ability to properly absorb folic acid, which is why a supplement is only a step in the right direction. In these cases, a major part of the solution is to stop drinking. Unfortunately, because alcohol anemia occurs in extreme cases of heavy drinking and alcohol abuse, stopping can be difficult. Not only does alcohol cause anemia, but it’s also a highly addictive depressant that can take over a person’s life. Simply quitting isn’t always an option for alcoholics unless they undergo residential addiction treatment. If you or someone you care about is currently struggling with drinking, our Christian drug rehab can help. We offer alcohol detox and treatment programs to address both the physical and psychological challenges of addiction. Although we offer faith-based recovery programs, our program welcomes people of all faith and non-faith backgrounds.
What Role Does Alcohol Play In Bone Marrow Suppression?
Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on the health of your bone marrow, which plays a crucial role in the body's ability to manage blood health. Bone marrow is essential for producing blood cells, including platelets, which are critical for blood clotting. When you suffer an injury, like a bloody nose, it's the platelets that help stop the bleeding.
1. Suppression of Platelet Production: Chronic alcohol use can suppress the bone marrow's ability to produce platelets. This reduction in platelet production impairs the blood clotting process, potentially leading to excessive bleeding during injuries.
2. Increased Risk of Hemorrhagic Strokes: Additionally, the decreased production of healthy platelets and other blood cells can heighten the risk of strokes that are caused by bleeding in the brain, known as hemorrhagic strokes.
In summary, alcohol can negatively affect bone marrow function, leading to lowered platelet counts and increased risks of serious health issues like excessive bleeding and strokes. It’s important for individuals consuming alcohol to understand these potential risks and manage their alcohol intake accordingly.
How does alcohol use affect the immune system and the human body?
The Impact of Alcohol Use on the Immune System and the Body Alcohol consumption can have significant repercussions on the human body, affecting various organs and systems. One of the less visible but crucial impacts is on the immune system, particularly how it hampers the production and function of the body's blood cells.
A Closer Look at Blood Cell Production
The body's immune defense relies heavily on the proper functioning and adequate production of blood cells, which occurs in the bone marrow. Here's how alcohol interferes:
- Reduction in White Blood Cells: These cells play a pivotal role in fighting off infections. Alcohol disrupts their production, leaving the body more susceptible to catching diseases.
- Decrease in Red Blood Cells: Responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body, a decrease in these cells can lead to fatigue and diminished vitality, affecting overall energy levels.
Other Body Functions Affected
- Liver: Frequent alcohol use can lead to liver diseases like cirrhosis, severely impairing the liver's ability to function and detoxify the body.
- Brain: Cognitive functions can diminish due to alcohol's effects on neurotransmitters, leading to impaired decision-making and memory loss.
- Heart: Excessive alcohol intake can escalate the risk of heart diseases, including arrhythmias and cardiomyopathy.
In conclusion, alcohol use does more than just damage the liver, brain, and heart; it reaches deep into the core mechanisms of the immune system, substantially diminishing the body’s ability to produce crucial blood cells. This disruption leaves an individual feeling weak, energy-depleted, and more open to infections, indicating how pervasive and detrimental alcohol can be to the human body.
What Are The Potential Risks And Complications Associated With Bone Marrow Suppression From Alcohol Use?
Alcohol use can have detrimental effects on bone marrow, leading to a range of risks and complications. When alcohol interferes with the bone marrow's ability to produce white and red blood cells, it can result in fatigue, weakness, and increased susceptibility to infections. Excessive drinking may lead to the destruction of both white and red blood cells, affecting blood clotting and raising the risk of excessive bleeding and strokes. Bone marrow suppression caused by alcohol consumption can also be linked to serious conditions such as Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Anemia, which is characterized by a decreased red blood cell count, is a common outcome of bone marrow suppression due to alcohol use. Symptoms of these complications may include fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, fever, chills, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, and easy bruising.
What Are The Different Types Of Blood Cells And Their Functions In The Body?
Blood contains three main types of cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen to all parts of the body, white blood cells help fight off infections, and platelets are essential for blood clotting. Alcohol use can interfere with the bone marrow's ability to produce these different types of blood cells. Excessive drinking can lead to the destruction of both white and red blood cells, affecting their production and functionality. Furthermore, alcohol can also impact the production of platelets in the bone marrow, which are crucial for blood clotting. This disruption in the production of blood cells can leave a person feeling tired, weak, and more vulnerable to infections. It can also increase the risk of excessive bleeding and strokes due to impaired blood clotting mechanisms.
How Can Bone Marrow Suppression Due To Alcohol Use Be Treated And Reversed?
Bone marrow suppression is a serious condition where the body's ability to produce blood cells is impaired, often exacerbated by long-term alcohol use. Fortunately, this condition can be treated and potentially reversed with appropriate medical intervention and lifestyle changes.
Comprehensive Treatment Approach
1. Medical Intervention: The first step in treating bone marrow suppression is to seek medical advice. Healthcare professionals may prescribe medications that can stimulate bone marrow to produce necessary blood cells. In severe cases, treatments might include blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants.
2. Abstinence from Alcohol: Stopping alcohol consumption is crucial. Continuous alcohol use can further damage bone marrow and negate the effects of any treatment.
3. Nutritional Support: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential. Specific nutrients that support bone marrow function include iron, vitamin B12, and folate. Doctors often recommend dietary adjustments or supplements to help.
4. Regular Monitoring: Recovery from bone marrow suppression involves regular check-ups. These allow doctors to track blood cell levels and adjust treatment plans as needed.
While the journey to recovery can be challenging, proper treatment and lifestyle modifications make bone marrow suppression manageable. Those affected are encouraged to contact healthcare providers to discuss their specific condition and tailor a recovery plan suited to their needs. Through diligent care and abstinence from alcohol, patients can work towards restoring their bone marrow health and overall well-being.
How Does Alcohol Use Disorder Affect Individuals According To A Study By Harvard University?
According to a study conducted by Harvard University, alcohol use disorder is defined as a condition where an individual experiences stress or harm due to their drinking habits. The study revealed that approximately 10% of adult men and 5% of adult women suffer from alcohol use disorder. This prevalence indicates that a significant proportion of the population is adversely affected by problematic alcohol consumption. Additionally, the study highlights the concerning statistic that alcohol is the second most widely used drug in the United States. It was also reported that around 88,000 individuals succumb to alcohol-related deaths in the country annually. These findings underscore the profound impact that alcohol use disorder can have on individuals, their families, and society as a whole.
How can Banyan's Faith In Recovery Program Assist Individuals Struggling With Substance Abuse, Including Alcohol Addiction?
Banyan's Faith In Recovery Program is dedicated to assisting individuals struggling with alcohol addiction and related issues by providing support and treatment through their alcohol treatment centers. If you or someone you know is facing a substance problem, reaching out to Banyan's Faith In Recovery Program can connect you with the help you need. By calling a Banyan's Faith In Recovery Program's alcohol treatment center, you can speak to a knowledgeable individual who can guide you towards the appropriate resources and support tailored to address alcohol addiction and related challenges effectively.
From medical detox to PHP addiction treatment, our rehab center is here to help. Call Faith in Recovery today at 888-280-4763 for more information about our faith-based drug treatment programs in Florida.
Related Reading:
Long-Term Effects of Alcohol on The Kidneys
High-Functioning Alcoholic: Signs and Symptoms

