
Dope Sick Symptoms & TV Show
June 29, 2022
Foods That Reduce Alcohol Cravings
July 21, 2022
Dope Sick Symptoms & TV Show
June 29, 2022
Foods That Reduce Alcohol Cravings
July 21, 2022
How Long Does Methylphenidate Stay In Your System?
Methylphenidate is a prescription stimulant that’s sold under brand names like Ritalin and Concerta. It was first licensed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1955, during which it was used mostly to treat hyperactivity, which is now known as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Over the decades, it’s been prescribed to people with ADHD ages 6 and older as a part of more comprehensive treatment for the disorder. While generally safe, it’s important to be aware of methylphenidate's side effects and reactions. In light of this, today we’re going to dissect the question: how long does methylphenidate stay in your system?
How Long Does Methylphenidate Last In Your System?
Factors That Influence How Long Ritalin Is in Your System
Certain factors can affect how long methylphenidate lasts in your body. This is the case with any drug. Body mass, weight, age, and liver and kidney function can all affect how quickly a drug leaves a person’s system. For instance, a heavier person may eliminate drugs more quickly than a lighter person.
Younger, healthier individuals also tend to excrete drugs more quickly than older people, those with kidney problems, and people with underlying health issues. A person’s metabolism can also impact how long methylphenidate will stay in their system, as well as their level of physical activity and hydration.
How Long Does Methylphenidate Stay In Urine, Hair, and Blood for Drug Tests?
Many people also wonder whether methylphenidate shows up on a drug test. While there is no specific methylphenidate drug test, it might show up on a screen paneling for amphetamines.
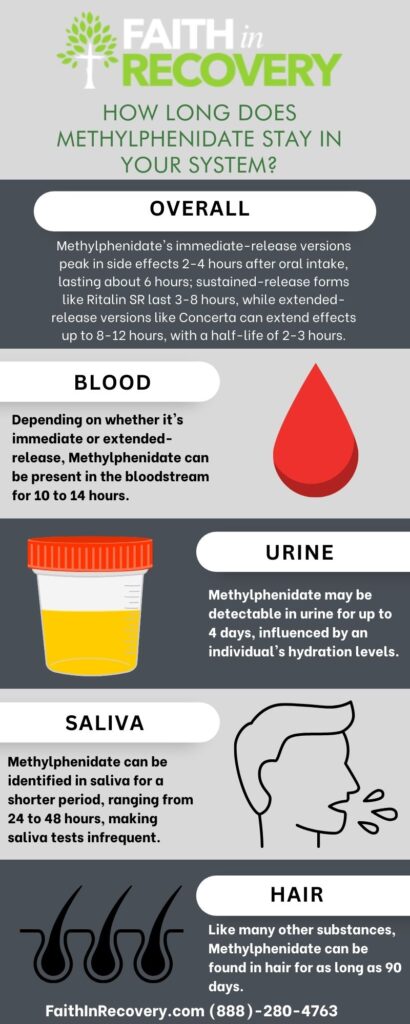
Methylphenidate is not likely to show up on a standard 5-panel drug screen, however. With that said, how long methylphenidate lasts in blood, urine, hair, and saliva varies.
-
Blood: Methylphenidate can be detected in blood for up to 10 to 14 hours, depending on its formulation (immediate versus extended-release.)
-
Urine: Methylphenidate can stay in urine for up to 4 days, depending on the person’s hydration levels and how much water they drink.
-
Saliva: Methylphenidate can also be detected in saliva for up to 24 to 48 hours, which is a shorter detection window than blood and urine tests. For this reason, saliva drug tests are rare.
-
Hair: As with other drugs, methylphenidate can be detected in hair for up to 90 days.
Why are blood tests not commonly used to screen for Ritalin?
Blood tests are not frequently utilized for screening Ritalin due to several reasons. One primary reason is that Ritalin's presence in the blood may not accurately reflect its therapeutic effect or indicate whether the drug is being used appropriately. Additionally, monitoring Ritalin levels through blood tests is not considered a reliable method for assessing an individual's response to the medication or predicting its efficacy. Furthermore, there are other more practical and effective ways to evaluate the use of Ritalin, such as clinical assessment and observation of behavioral changes. Therefore, the limited utility and reliability of blood tests in screening for Ritalin usage contribute to their infrequent use for this purpose.
How is methylphenidate used to treat ADHD and other conditions?
Methylphenidate is a stimulant medication typically prescribed to manage symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and certain other conditions. This medication primarily works by enhancing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, namely dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play crucial roles in attention and behavior regulation.
How Methylphenidate Works
- Increases Brain Activity: Methylphenidate boosts the activity within the brain and spinal cord, increasing alertness and concentration.
- Reduces ADHD Symptoms: Despite ADHD being characterized by hyperactivity and impulsiveness, methylphenidate helps lower these behaviors, improving focus and reducing impulsivity.
- Supports Neurological Function: In individuals with ADHD, the brain may exhibit less activity in certain areas that control attention and motion. Methylphenidate helps mitigate this imbalance, fostering better cognitive and behavioral performance.
Long-Term Benefits
Research suggests significant long-term benefits for those with ADHD who are treated with medications such as methylphenidate. These benefits include:
- Enhanced educational achievements
- Improved occupational success
- Lower instances of substance abuse
By addressing the underactive brain states associated with ADHD, methylphenidate supports individuals in achieving better overall functionality and quality of life.
How is methylphenidate abused, and what are the potential consequences of misuse?
Methylphenidate, specifically medications like Ritalin, poses a significant risk of abuse. It is commonly misused in various settings, with one prevalent misuse involving using the drug as a cognitive or performance enhancer. This misuse often involves actions such as grinding the pills to snort the powder, or taking larger doses than prescribed to study for exams or stay awake for extended periods. Notably, individuals in high-pressure academic or professional environments may also misuse these stimulants to enhance their performance and prolong their wakefulness. While there is a perception that substances like Ritalin can enhance cognitive abilities, research indicates that this belief may be exaggerated.
While stimulants, including caffeine, can temporarily improve focus and attention when consumed in moderate amounts, misuse or taking large doses of these substances can have adverse effects, such as reducing attention span. It is important to note that these drugs do not inherently boost intelligence. Studies suggest that individuals who abuse Ritalin and similar substances may have lower levels of academic and professional achievements compared to non-users.
How does Ritalin treatment impact individuals with ADHD in terms of long-term outcomes?
Ritalin treatment has been found to have positive long-term outcomes for individuals with ADHD. Studies suggest that individuals with ADHD may have an underactive brain in their resting state, leading to attention deficits and impulsivity. By treating ADHD with stimulant medications like Ritalin, individuals have shown improvements in educational achievement, occupational success, and reduced issues with substance abuse in the long term. This indicates that Ritalin treatment can positively impact the lives of individuals with ADHD by addressing their symptoms and supporting their overall development and well-being over time.
How do central nervous system stimulants like Ritalin affect neurotransmitters in the brain?
Central nervous system stimulants such as Ritalin have an impact on neurotransmitters in the brain by interacting with chemicals like dopamine, norepinephrine, and various others that are vital for neuron communication in the brain. These medications influence the levels and activities of these neurotransmitters, thereby affecting how messages are transmitted between neurons and ultimately modulating various brain functions and behaviors.
How does age impact the elimination of methylphenidate from the body?
Age is a significant factor that influences the elimination of methylphenidate from the body. Generally, older individuals metabolize and eliminate the drug at a slower rate compared to younger individuals. This difference is attributed to age-related changes in metabolism, organ function, and overall physiological processes, which affect the body's ability to process and clear methylphenidate efficiently. The impact of age on drug elimination underscores the importance of considering individual variations, especially in dosing and treatment strategies, based on age-related factors to ensure drug efficacy and safety in different age groups.
What are the different forms of Ritalin available?
Ritalin has evolved over time to be available in multiple formats to better cater to the needs of those requiring medication for ADHD. Initially, Ritalin was only offered in an immediate-release formula, which provided quick relief from symptoms but required multiple doses throughout the day. To provide more flexibility and convenience, new formulations were developed:
-
Slow-Release Ritalin: This formulation releases the active ingredient, methylphenidate, gradually over time, reducing the number of doses a person needs to take in a day.
-
Extended-Release Ritalin: This type lasts even longer than the slow-release variant, making it a once-daily medication. It works by releasing a steady amount of methylphenidate throughout the day.
Another option available is Concerta, a specific brand of medication that also contains methylphenidate but is exclusively available in an extended-release form. Concerta has been approved by the FDA specifically for the treatment of ADHD, providing a long-lasting option for managing symptoms effectively.
Why is Ritalin classified as a controlled substance by the DEA?
Ritalin, which contains methylphenidate, is regulated under Schedule II of the DEA's controlled substances list. This classification indicates that while Ritalin has valid medical uses, it also poses a substantial risk for abuse and dependency. The strict regulation under Schedule II is due to these dual factors: recognized medicinal value and potential for misuse. Consequently, Ritalin must be prescribed by a doctor and its usage closely monitored, ensuring it is used safely and responsibly. This balance attempts to allow access to those in need while minimizing potential harm from abuse.
Where can one find drug and alcohol rehab treatment facilities near them?
If you or a loved one is addicted to ADHD medications like methylphenidate, call Faith in Recovery at 888-280-4763. Our Christian residential drug rehab offers various forms of substance-specific treatment to provide clients with individualized care for their physical and psychological recovery from addiction.

